I’m still working on the “Taxonomy of Yogurt” post which I currently plan to do next, but I’m overdue for a post already – therefore, here’s a brief one to keep my legion of adoring fans appeased until the next long post, here’s a short one.
Part 1: I got an interesting search-query hit recently – looks like (I’m guessing) a technician working at a famous pharmaceutical/healthcare-product company ran into the same problem I did during my current Bacterial Virology lab – “chunky microbiology agar in microwave”.
Agar is nifty stuff to use for microbiology. Dried, it’s a lumpy powder. To use it, you dump around 1-2% w/v (more or less, depending on the consistency of agar that you need) into water and heat it up to dissolve it. It’s basically seaweed-JellO™ – except it’s not actually affiliated with Kraft Foods nor made of gelatin. Anyway – once it’s dissolved, it’ll cool into a gel.
The nice thing is, you can make up a bottle of this stuff and let it solidify, and store it (sealed) for quite a while. When you want to use it, you can just stick it in a microwave oven to melt it back down. It has to get pretty hot for this, but it then stays liquid until it gets down nearer to room temperature, so you’ve got plenty of time to pour it into plates or tubes or whatever.
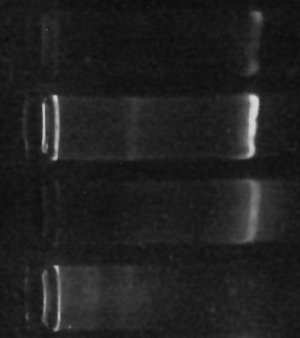
For bacterial virology purposes, we make up a “soft agar” (about 0.8% agar, as I recall) to make an “overlay” – after mixing bacteria and virus together into a small amount of melted [but mostly cooled, so it doesn’t fry the bacteria] agar, we pour the soft agar in a thin layer over the top of a regular layer of nutrient agar in a plate. (The idea is that then wherever there is a virus that can infect and kill bacteria, it’ll wipe out all the bacteria growing in a particular part of the overlay, leaving a cleared “plaque” – you can then count how many plaques there are to find out how many virus were in the original sample, for example).
Earlier this semester, we had a fair amount of trouble with this. We’d go to pour the overlay and it’d come out chunky, even though it looked completely melted when we prepared it. Fortunately, the problem is simple and easily solved – you just need to nuke the heck out of the stuff, frequently swirling the container to make sure it’s completely mixed. What seems to be happening is that a few bits of agar remain unmelted but hard to see if you’re not careful, and those bits allow the melted agar to coagulate around them more readily. In short, the trick is to make really sure that all of the agar is completely melted.
Note that you have to be careful while doing this – lots of bubbles end up coming out of the agar when you swirl it, and it can easily foam out of the container and burn your hand. (Oh, obviously you also need to leave the lid a little loose to let off the pressure.) Of course, the stuff will be really hot when you’re done with the microwave, but as mentioned before, it’ll stay liquid until it is much cooler before it solidifies. If you set the bottle in a warm-water bath (~50°C or so) you can basically walk away for hours, leave it overnight, or whatever, and it should still be completely liquid and smoothly pourable – not to mention cool enough to handle with bare hands – when you get back.
And on the subject of gelled material – the fact that I mentioned all the hits about expired Jell-O™ in the previous post seems to have substantially increased the number of “expired-JellO™-related” hits I’ve gotten, so here’s a slightly more expanded update.
Assuming one is referring to the “instant gelatin” powders (regardless of brand), as far as I can tell they ought to be safe to use almost indefinitely. Officially, Kraft Foods, the owners of the Jell-O™ trademark say that the expected shelf-life is 2 years (“24 months”). I still think, personally (Note – Your Mileage May Vary, Do Not Try This At Home, and other standard disclaimers apply here) just like sugar, that it is probably safe to use practically forever as long as it doesn’t get wet (and isn’t stored in humid conditions). I don’t think anything of consequence would be able to grow on the dry powder, and I find it unlikely that the normal flavorings would be prone to suddenly become poisonous as a result of ordinary aging. The only thing you might have to worry about is maybe some of the flavoring compounds getting slowly oxidized by the air, so maybe the result wouldn’t taste quite the same. As far as I am concerned, so long as there weren’t fuzzy clumps growing in it, if the contents of the packet were still flaky/powdery, I’d most likely go ahead and use it, and not expect to suffer any ill effects.
‘course, if you read my obituary someday and it notes that I died of expired-gelatin-poisoning, you’ll know I was wrong…
UPDATE: I empirically test the toxicity of of expired JellO® on my own body! The saga begins here!